Statistics
2021 Cyber Security Statistics The Ultimate List Of Stats, Data & Trends
Cybercrime Up 600% Due To COVID-19 Pandemic
Due to the COVID-19 outbreak an uptick in sophisticated phishing email schemes by cybercriminals has emerged. Malicious actors are posing as the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or World Health Organization (WHO) representatives.
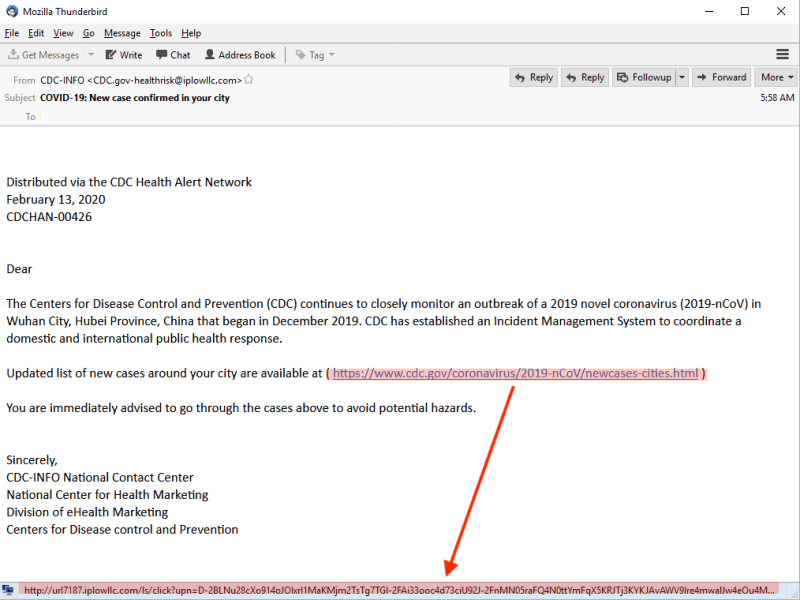
These emails are designed to deceive and trick recipients into taking an action such as clicking a malicious link, or opening an attachment with a virus. Learn what steps you can take to help prevent phishing attacks
Network Security Vulnerabilities
Anetwork security vulnerability is a weakness or flaw which can be exploited by a malicious actor to perform unauthorized actions within a computer system.
Malware Statistics
Malware, or malicious software, is any piece of software that was written with the intent of doing harm to data, devices or to people. Types of malware include computer viruses, trojans, spyware, ransomware, adware, worms, file-less malware, or hybrid attacks. Recent malware attacks have bencome more sophisticated with the advent of machine learning and targeted spear phishing emails.
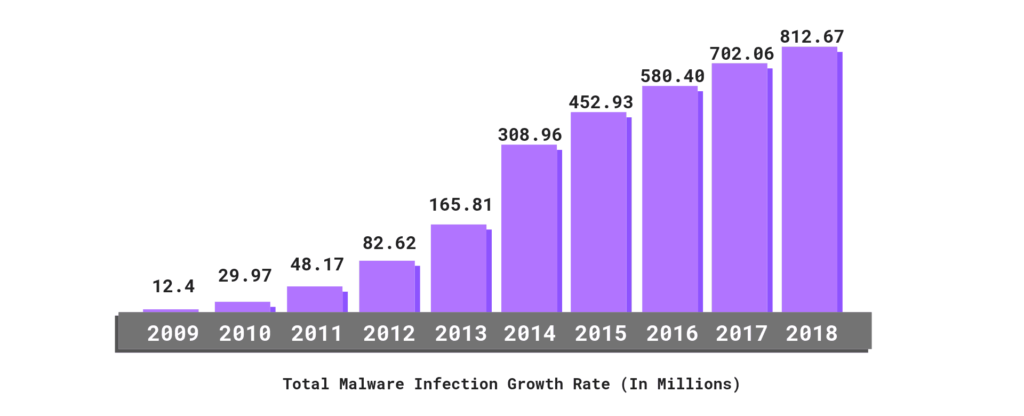
The total malware infections have been on the rise for the last ten years:
2009 – 12.4 million
2010 – 29.97 million
2011 – 48.17 million
2012 – 82.62 million
2013 – 165.81 million
2014 – 308.96 million
2015 – 452.93 million
2016 – 580.40 million
2017 – 702.06 million
2018 – 812.67 million
- 92% of malware is delivered by email.
- Mobile malware on the rise with the number of new malware variants for mobile increased by 54% in 2018.
- Third-party app stores host 99.9% of discovered mobile malware.
- More than 250,000 unique users were attacked by Trojan-Banker.AndroidOS.Asacub malware application.
- 98% of mobile malware target Android devices.
- Over the last year, MacOS malware has increased by 165%.
- Malware development rates for Windows decreased by 11.6% since reaching an all-time high in 2015.
- Malware is still the preferred distribution model, used 71.14% of the time over the last 12 months, while PUAs were only used in 28.86% of instances.
- Gamut spambot was the most frequently used, with over 86% of all spambot cases involving its use.
- The United States continues to host the most botnet control servers in the world. Over the last year, 36% of these servers were hosted in America, while 24% were hosted in undefined countries.
- Trojans make up 51.45% of all malware.
- 7 out of every 10 malware payloads were ransomware.
- 230,000 new malware samples are produced every day — and this is predicted to only keep growing.
- Malware and web-based attacks are the two most costly attack types — companies spent an average of US $2.4 million in defense.
- Overall business detections of malware rose 79% from 2017 due to an increase in backdoors, miners, spyware, and information stealers.
- Over 18 million websites are infected with malware at a given time each week.
- 34% of businesses hit with malware took a week or more to regain access to their data.
- 90% of financial institutions reported being targeted by malware in 2018.
Ransomware Statistics
Ransomware is a form of malicious software that threatens you with harm, usually by denying you access to your data. Ransomware attacks are often deployed via social engineering tacitics. Once a user falls victim to the attack, their data is encrpyted. The attacker then demands a ransom from the victim, with the promise to restore access to the data upon payment.
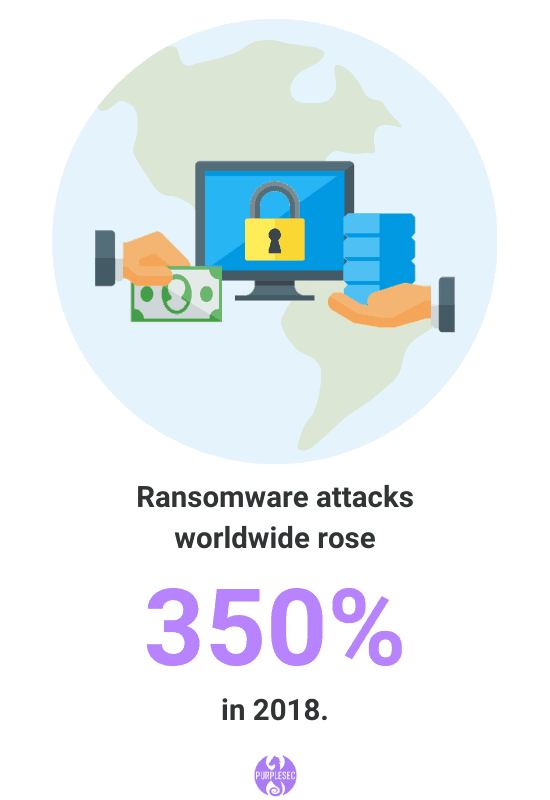
- Ransomware attacks worldwide rose 350% in 2018.
- Ransomware attacks are estimated to cost $6 trillion annually by 2021.
- 50% of a surveyed 582 information security professionals do not believe their organization is prepared to repel a ransomware attack.
- 81% of cyber security experts believe there will be more ransomware attacks than ever in 2019.
- 75% of companies infected with ransomware were running up-to-date endpoint protection.
- Ransomware costs businesses more than $75 billion per year.
- The NotPeyta ransomware attack losses could exceed $1 billion.
- FedEx lost an estimated $300 million in Q1 2017 from the NotPetya ransomware attack.
- Atlanta, Georgia has spent more than $5 million rebuilding its computer network, after being hit by the SamSam ransomware attack in March 2018.
- The average cost of a ransomware attack on businesses was $133,000.
- Businesses lost around $8,500 per hour due to ransomware-induced downtime.
- 25% of business executives would be willing to pay between $20,000 and $50,000 to regain access to encrypted data
- 30% of organizations who pay the ransom receive all of their money back.
- 40% of ransomware victims paid the ransom.
- More than 50% of ransoms were paid by bitcoin in 2018.
- 10% of all ransom demands are over $5,000.
- Of the 1,100 IT professionals surveyed, 90% had clients that suffered ransomware attacks in the past year.
- 40% had clients that were subject to at least 6 ransomware attacks.
- A new organization will fall victim to ransomware every 14 seconds in 2019, and every 11 seconds by 2021.
- 1.5 million new phishing sites are created every month.
- In 2019 ransomware from phishing emails increased 109% over 2017.
Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking is the unauthorized use of someone else’s computer to mine cryptocurrency. Hackers do this by getting the victim to click on a malicious link in an email that loads crypto mining code on the computer, or by infecting a website with JavaScript code that executes once loaded in the victim’s browser.
- 25% of businesses are estimated to have been victims of cryptojacking
- Cryptojacking activity surged to its peak in December 2017, when more than 8 million cryptojacking events were blocked by Symantec.
- 25% of the WordPress plugins among Alexa’s most popular sites are flagged with critical vulnerabilities that could allow mining botnets in.
- Applications can take 5 – 10 longer to load when a computer is being used for coin mining.
Social Engineering Statistics
Social engineering in cyber security is the psychological manipulation of people into performing actions or divulging confidential information. Candidates for a social engineering attack can range from a corporate executive to an elementary school student. Even the most seasoned IT professional can be victimized by this type of attack.
- 98% of cyber attacks rely on social engineering.
- 43% of the IT professionals said they had been targeted by social engineering schemes in the last year.
- New employees are the most susceptible to socially engineered attacks, with 60% of IT professionals citing recent hires as being at high risk.
- 21% of current or former employees use social engineering to gain a financial advantage, for revenge, out of curiosity or for fun.
- Social engineering attempts spiked more than 500% from the first to second quarter of 2018.
- The number of breach incidents by type:
- Identity theft – 65%
- Account access – 17%
- Financial access – 13%
- Nuisance – 4%
- Existential data – 1%
- The number of breach incidents by source:
- Malicious outsider – 56%
- Accidental loss – 34%
- Malicious insider – 7%
- Hackivist – 2%
- Unknown – 1%
- Numbers of records breached by industry in 2018:
- Social media: 2.5 billion records, or 56%
- Government: 1.2 billion records, or 27%
- Other industries: 380 million records, or 8%
- Retail: 186 million records, or 4%
- Technology: 171 million records, or 4%
Phising Statistics
Phishing is a type of cyber attack where threat actors randomly send emails to a broad audience in an attempt to trick people into providing sensitive information such as account credentials or sensetive information.
- 56% of IT decision makers say targeted phishing attacks are their top security threat.
- 83% of global infosec respondents experienced phishing attacks in 2018, an increase from 76% in 2017.
- Business email compromise (BEC) scams cost organizations $676 million in 2017.
- CEO fraud is now a $12 billion scam.
- 30% of phishing messages get opened by targeted users and 12% of those users click on the malicious attachment or link.
- Only 3% of targeted users report malicious emails to management.
- 53% of IT and security professionals say they have experienced a targeted phishing attack in 2017.
- Credential compromise rose 70% over 2017, and they’ve soared 280% since 2016.
- 50% of phishing sites now using HTTPS.
- Fake invoices are the #1 disguise for distributing malware.
- Bill / invoice 15.9%
- Email delivery failure 15.3%
- Legal / law enforcement 13.2%
- Scanned document 11.5%
- Package delivery 3.9%
- The most common malicious attachment types:
- Office 38%
- Archive 37%
- PDF 14%
- Other Ext 6%
- Binaries 4%
- XML/HTML/JS 1%
- The volume of email fraud that organizations receive has increased 8% year-over-year.
- By the end of 2017, the average user was receiving 16 phishing emails per month.
- 66% of malware is installed via malicious email attachments.
- 49% of non-point-of-sale malware was installed via malicious email.
- 21% of ransomware involved social actions, such as phishing.
- 30% of phishing messages were opened in 2016 – up from 23% in the 2015 report.
General Cyber Security Statistics
The Cost Of Cyber Security
- In 2017, cyber crime costs accelerated with organizations spending nearly 23% more than 2016 — on average about $11.7 million.
- By 2020, we expect IT analysts covering cyber security will be predicting five-year spending forecasts (to 2025) at well over $1 trillion.
- The average cost of a malware attack on a company is $2.4 million.
- The average cost in time of a malware attack is 50 days.
- From 2016 to 2017 there was a 22.7 % increase in cyber security costs.
- The average global cost of cyber crime increased by over 27% in 2017.
- The most expensive component of a cyber attack is information loss, which represents 43% of costs.
- Ransomware damage costs exceed $5 billion in 2017, 15 times the cost in 2015.
- The Equifax breach cost the company over $4 billion in total.
- The average cost per lost or stolen records per individual is $141 — but that cost varies per country. Breaches are most expensive in the United States ($225) and Canada ($190).
- Including turnover of customers, increased customer acquisition activities, reputation losses and diminished goodwill the cost of lost business globally was highest for U.S. companies at $4.13 million per company.
- Damage related to cybercrime is projected to hit $6 trillion annually by 2021.
Data Breach Statistics
- The average cost of a data breach to companies worldwide is $3.86 million.
- It takes organizations an average of 191 days to identify data breaches.
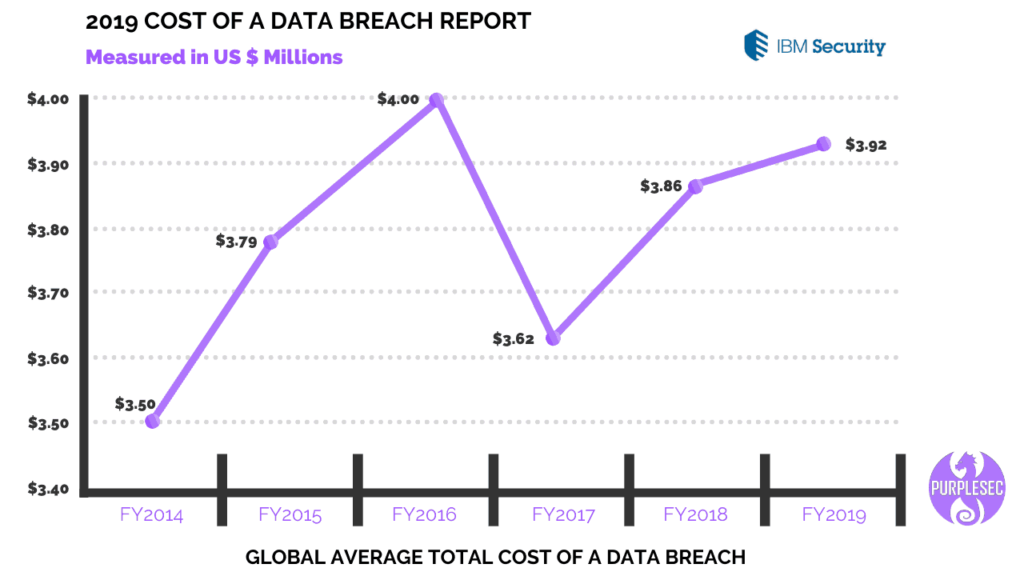
- Global average total cost of a data breach (in millions):
- 2014 – $3.50
- 2015 – $3.79
- 2016 – $4.00
- 2017 – $3.62
- 2018 – $3.86
- 2019 – $3.92
- The root causes of data breaches for small businesses broke out as following:
- Negligent employee or contractor 48%
- Third party mistakes 41%
- Error in system or operating process
- Don’t know
- External (hacker) attacks 27%
- Malicious insider 5%
- Other 2%
- 95% of breached records came from three industries in 2016:
- Government
- Retail
- Technology
- Recent data breach statistics found that 63% of successful attacks come from internal sources, either control, errors, or fraud.
- 33% of data breaches involved social engineering.
- 43% of data breaches involved small businesses.
- The average size of a data breach is 25,575 records.
- The total number of breaches in 2019 was 1,473, up from 1,257 the year before. 164.6 million records were exposed in 2018.
- The average cost per lost record is $150.
- Targeted emails, or spear phishing, is reported by businesses to be used in 91% of successful data breaches and 95% of all enterprise networks.
- Half of all data breaches globally to occur in the United States by 2023.
- 29.6% of companies will experience a data breach in the next two years.
- In 2019, the number of data breaches in the United States amounted to 1,473 with over 164.68 million sensitive records exposed.
- The United States and the Middle East spend the most on post-data breach response. Costs in the U.S. were $1.56 million and $1.43 million in the Middle East.
- In companies with over 50k compromised records, the average cost of a data breach is $6.3 million.
- The average cost of lost business for organizations in the 2019 study was $1.42 million, which represents 36 percent of the total average cost.
- The impact of a data breach is disproportionately larger for smaller organizations between 500 and 1,000 employees at an average cost of $2.65 million, or $3,533 per employee.
- Breaches caused a customer turnover of 3.9% in 2019.
- Email compromises cost on average $24,439 per case.
- 36% of breaches were in the medical or healthcare industry in 2019.
- Healthcare organizations have the highest average industry cost at $6.45 million.
- Healthcare data breaches are costing the US industries $6.2 billion per year.
- 69% of those in the healthcare industry believe they are at great risk for a data breach than other industries.
- Banks were the target 47% of financial data breaches.
- The financial sector experienced 137 breaches in 2018 that exposed 1.7 million accounts.
- Share prices of breached companies hit a low point approximately 14 market days following a breach. Share prices fall 7.27% on average, and underperform the NASDAQ by -4.18%.
Cyber Security Risks
- In 2018 there were 80,000 cyber attacks per day or over 30 million attacks per year.
- 21% of all files are not protected in any way.
- 41% of companies have over 1,000 sensitive files including credit card numbers and health records left unprotected.
- 70% of organizations say that they believe their security risk increased significantly in 2017.
- 69% of organizations don’t believe the threats they’re seeing can be blocked by their anti-virus software.
- 50% of the security risk that organizations face stems from having multiple security vendors and products.
- 7 out of 10 organizations say their security risk increased significantly in 2017.
- 65% of companies have over 500 users who never are never prompted to change their passwords.
- Ransomware attacks are growing more than 350% annually.
- IoT attacks were up 600% in 2017.
- 61 percent of breach victims in 2017 were businesses with under 1,000 employees.
- Ransomware damage costs will rise to $11.5 billion in 2019 and a business will fall victim to a ransomware attack every 14 seconds at that time.
- 2017 represented an 80% increase in new malware on Mac computers.
- In 2017 there was a 13% overall increase in reported system vulnerabilities.
- 2017 brought a 29% Increase in industrial control system–related vulnerabilities.
- Coin mining represented the biggest growth area in cybercrime in 2017, with antivirus detections up 8,500%
- 90% of remote code execution attacks are associated with crypto mining.
- Over 50 Internet of Things commercially available devices shares security vulnerabilities.
- 61% of organizations have experienced an IoT security incident.
- 77% of compromised attacks in 2017 were fileless.
- 69% of companies see compliance mandates driving spending.
- 88% of companies spent more than $1 million on preparing for the GDPR.
- 25% of organizations have a standalone security department.
- 54% of companies experienced an industrial control system security incident.
- Cyber criminals will steal an estimated 33 billion records in 2023.
- In 2017 there were over 130 large-scale, targeted breaches in the U.S. per year, and that number is growing by 27% per year.
- 31% of organizations have experienced cyber attacks on operational technology infrastructure.
- 100,000 groups in at least 150 countries and more than 400,000 machines were infected by the Wannacry virus in 2017, at a total cost of around $4 billion.
- In 2017 5.4 billion attacks by the WannaCry virus were blocked.
- There are around 24,000 malicious mobile apps blocked every day.
- In 2017, the average number of breached records by country was 24,089. The nation with the most breaches annually was India with over 33k files; the US had 28.5k.
- Between January 1, 2005 and April 18, 2018 there have been 8,854 recorded breaches.
Recent Cyber Attacks And Breaches
As data breaches become more pervasive in our interconnected world so must our understanding of modern day cyber attacks.
In this video series, we sit down with cyber security experts and get their take on the most recent cyber attacks and breaches in 2021.
- 2021 – Kaseya suffered a ransomware attack compromising up to 1500 companies with a staggering ransom note of $70 million.
- 2021 – Saudi Aramco experienced a data breach exposing sensitive data on employees and technical specifications of the organization. Threat group ZeroX is demanding a payment of $50 million.
- 2021 – The Accellion file transfer application (FTA) data breach impacted over 100 companies, organizations, universities, and government agencies around the world.
- 2021 – The Pulse Secure VPN zero-day was exploited resulting in the breach of several undisclosed defense firms and government organizations in the United States and Europe.
- 2021 – =Solarwinds fell victim to a nation-state supply chain attack impacting government agencies and fortune 500 companies.
- 2020 – The hotel chain Marriott disclosed a security breach that impacted the data of more than 5.2 million hotel guests who used their company’s loyalty application.
- 2020 – MGM Resorts suffered a massive data breach resulting in the leak of 142 million personal details of hotel guests.
- 2020 – 500,000 stolen Zoom passwords available for sale in dark web crime forums.
- 2020 – Magellan Health was struck by a ransomware attack and data breach stating that 365,000 patients were affected in the sophisticated cyberattack.
- 2020 – Twitter breach well-coordinated scam made attackers swindle $121,000 in Bitcoin through nearly 300 transactions.
- 2019 – Maryland Department of Labor was breached by hackers who illegally accessed names and social security numbers belonging to 78,000 people.
- 2019 – Captical One recently had over 106 million records stolen containing personal and financial information.
- 2018 – Cyber attackers hacked into Marriot international computer systems and compromised five hundred million accounts.
- 2018 – Cathy pacific was hacked and 9.4 million accounts compromised.
- 2018 – Facebook code was exploited by attackers and 50 million user accounts compromised.
- 2018 – Quora was hacked and information belonging to 100million users compromised.
- 2018 – Under Armor reported that its “My Fitness Pal” was hacked, affecting 150 million users.
- 2017 – Uber network was breached compromising data of fifty million riders, seven million drivers and 600,000 US based driver license details.
- 2017 – Cyber attackers hacked into Equifax servers and exposed over 143 million consumers’ personal information.
- 2017 – 412 million user accounts were stolen from Friendfinder’s sites.
- 2017 – 147.9 million consumers were affected by the Equifax Breach.
- 2016 – Peace cyber-attackers hacked Myspace compromising over 360 million accounts.
- 2016 – Uber reported that hackers stole the information of over 57 million riders and drivers.
- 2015 – Hackers broke into Anthem Inc. servers and stole 37.5 million records consisting of sensitive information.
- 2015 – Peace a Russian based Cyber-attack group infiltrated LinkedIn stealing email and password combinations of over 117 million customers.
- 2014 – Syrian Electronic Army cyber hacking group infiltrated eBay’s network stealing sensitive information of one hundred and forty-five million users.
- 2013 – Cyber criminals hacked Yahoo’s 3 billion email accounts gaining access to sensitive customer information.
- 2013 – Cyber attackers used malware to steal data from Target company point of sale systems compromising information of approximately one hundred and ten million credit/debit carrying customers.
Federal And Local Government
- Over 70,000 Department of Defense contractors are required to meet CMMC compliance by 2021.
- Nearly 60 million Americans have been affected by identity theft.
- U.S. government to spend $15 billion on cyber security related activities in 2019 up 4% over the previous year.
- The United States is the number one target for targeted cyber attacks.
- United States: 38%.
- India: 17%.
- Japan: 11%.
- Taiwan: 7%.
- Ukraine: 6%.
- South Korea: 6%.
- Brunei: 4%.
- Russia: 4%.
- Vietnam: 4%.
- Pakistan: 3%.
Small Businesses
- 43% of cyber attacks target small business.
- 47% of small businesses had at lease on cyber attack in the past year, 44% of those had two to four attacks.
- 70% of small businesses are unprepared to deal with a cyber attack.
- 3 out of 4 small businesses say they don’t have sufficient personnel to address IT security.
- 66% of small business are very concerned about cyber security risk.
- 85% of small businesses plan to increase spending on managed security services.
- 51% of small businesses say they are not allocating any budget to cyber security.
- 58% of malware attack victims are categorized as small businesses.
- In 2018, cyber attacks cost small businesses an average of $34,604.
- Ransomware damage costs alone are on track to hit $11.5 billion in 2019, at which point it’s estimated that small businesses will fall victim to a ransomware attack every 14 seconds.
- 4% of malware sent to small businesses is delivered via email.
- The most common malicious email disguises are:
- 7% bill / invoice
- 3% email delivery failure notice
- 4% package delivery
- 1.1% legal/law enforcement message
- 0.3% scanned document
- 60% of small businesses say attacks are becoming more severe and more sophisticated.
- Only 14% of small businesses rate their ability to mitigate cyber risks, vulnerabilities and attacks as highly effective.
- 60% of small companies go out of business within six months of a cyber attack.
- 48% of data security breaches are caused by acts of malicious intent. Human error or system failure account for the rest.
- Small businesses are most concerned about the security of customer data:
- Consumer records 66%
- Intellectual property 49%
- Customer credit or debit card information 46%
- Financial information 26%
- Employee records 8%
- Business correspondence 5%
- Other 1%
- The types of cyber attacks on small businesses broke out as following:
- Web-based attack 49%
- Phishing / social engineering 43%
- General malware 35%
- SQL injection 26%
- Compromised / stole devices 25%
- Denial of services 21%
- Advance malware / zero day attacks 14%
- Malicious insider 13%
- Cross-site scripting 11%
- Ransomware 2%
- Other 1%
- Percentage of small businesses that store valuable data
- 68% store email addresses
- 64% store phone numbers
- 54% store billing addresses
- Small businesses are not investing in cyber security
- 38% regularly upgrade software solutions
- 31% monitor business credit reports
- 22% encrypt databases
- 69% of small businesses do not strictly enforce password policies.
- 16% of small businesses say they had only reviewed their cyber security posture after they were hit by an attack.
- Only 16% of small business are very confident in their cyber security readiness. These areas are lacking:
- Strategy – 52% of small business have a clearly defined strategy around cyber security.
- Accountability – 23% of small businesses have a leadership role dedicated to cyber, whereas 46% have no defined role at all.
- Willingness to respond – 65% of small businesses have failed to act following a cyber security incident.
- Training – 32% of small businesses have conducted phishing experiments to assess employee behavior and readiness in the event of an attack.
- Insurance – 21% of small businesses have a standalone cyber insurance policy, compared to 58% of large companies.
- 4 out of 5 small businesses report malware has evaded their antivirus.
Financial Institutes
- 67% of financial institutions reported an increase in cyber attacks over the past year.
- 26% of financial enterprises faced a destructive attack.
- 79% of financial CISOs said threat actors are deploying more sophisticated attacks.
- 21% suffered a watering-hole attack in the last year.
- 32% of financial institutions encountered island hopping, is leveraging one compromised organization to gain entry into another.
- 25% of all malware attacks hit banks and other financial industries, more than any other industry
- Credit card compromised increased by 212% year over year, credential leaks experienced a similar increase of 129%, and malicious apps increased by 102%.
- 47% of financial institutions reported an increase in wire transfer fraud.
- 31% of financial institutions reported an increase in home equity loan fraud.
- 79% of financial institutions said cybercriminals have become more sophisticated, leveraging highly targeted social engineering attacks.
- 32% of financial institutions reported experiencing counter incident response.
- 21% of financial institutions reported experiencing C2 on a sleep cycle.
- 70% of financial institutions said they are most concerned about financially motivated attackers.
- 30% of financial institutions said they are most concerned with nation-state activity.
- Global attack types and sources on financial sectors:
- Web attacks – 46%
- Service-specific attacks – 28%
- DoS/DDoS 8%
- 69% of financial institution CISOs are planning to increase cyber security spending by 10% or more in 2019.
- 47% of financial institution CISOs said their organizations are operating threat hunt teams.
- 32% of financial institution CISOs said they conduct threat hunts on a monthly basis.
- 70% of cyber crimes targeting surveyed financial institutions involve lateral movement.
Healthcare Providers
- 16% of healthcare providers report having “fully functional” security programs.
- 43% admitted that they are either still developing security programs or have not developed one.
- 93% of healthcare organizations are currently using some form of cloud services.
- 63% plan to use multiple cloud vendors.
- 20% of healthcare domain emails were fraudulent in 2017.
- Healthcare has the highest number of attacks by ransomware over any other industry.
- 82% of surveyed healthcare organizations say that security is a top concern.
- The average cost of a cyber attack in healthcare is $3.62 million.
- 89% of healthcare organization had patient data lost or stolen in the past two years.
- Patient health records can be sold for as much as $363 on the black market which is more than any piece of information from other industries.
- 54% of healthcare business associates say their top vulnerability is tied to employee negligence in handling patient information.
- 81 percent of healthcare cyber security incidents are rooted in employee negligence.
- 69% of healthcare organizations site negligent or careless employees as their top worry for security incidents, followed by cyber attacks (45%) and insecure mobile devices (30%).
- The healthcare industry was the victim of 88%of all ransomware attacks in US industries in 2016.
- 94% are now using some form of advanced technology to protect sensitive data.
- 25% healthcare organizations using the public cloud report that they are not encrypting patient data.
Higher Education And School Districts
- The education industry is ranked last in cyber security preparedness out of 17 major industries.
- 41% of higher education cyber security incidents and breaches were caused by social engineering attacks.
- There were 455 cyber security incidents in the educational sector last year.
- Educational records can fetch up to $265 on the black market.
- 43% have had student data attacked, including dissertation materials and exam results.
- 25% have experienced critical intellectual property theft.
- 28% have had grant holder research data attacked.
- 87% have experienced at least one successful cyber attack.
- 83% believe cyber attacks are increasing in frequency and sophistication.
- 79% universities have experienced damage to reputation and almost 74% have had to halt a valuable research project as a result of a cyber attack.
- 77% also say a cyber breach has the potential to impact national security, due to the potentially sensitive nature of the information which could been compromised.
- 64% don’t believe their existing IT infrastructure will protect them against cyber attacks in next 12-18 months.
- 27% see the current security of their data center as ‘inadequate’ and in urgent need of updating.
- 85% of universities agree that more funding must be given to IT security to protect critical research IP.
- On average, 30% of users in the education industry have fallen for phishing emails.
- The education sector accounted for 13% of all data security breaches during the first half of 2017, resulting in the compromise of some 32 million personal records.
- In March 2018, over 300 universities worldwide suffered from a giant cyber attack organized by nine Iranian hackers. According to the official information, 31 terabytes of “valuable intellectual property and data” was exposed.